Combi Piles in Retaining Wall Engineering: Cost and Schedule Advantages Explained
Introduction to Combi Piles
Definition & Typical Configuration
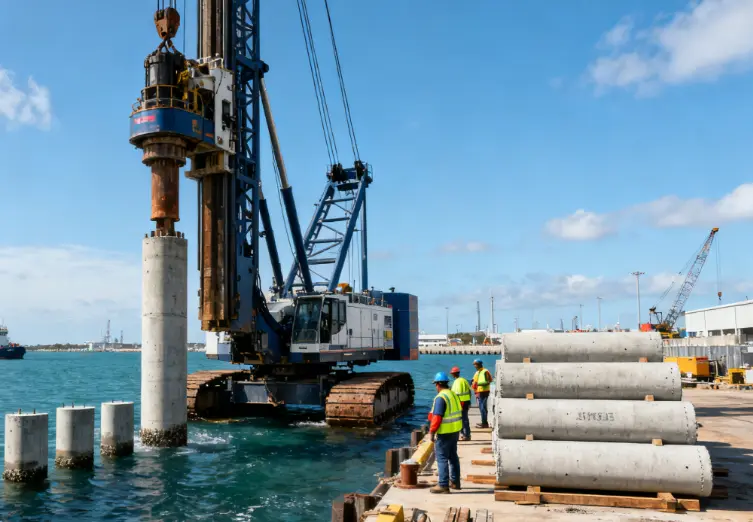
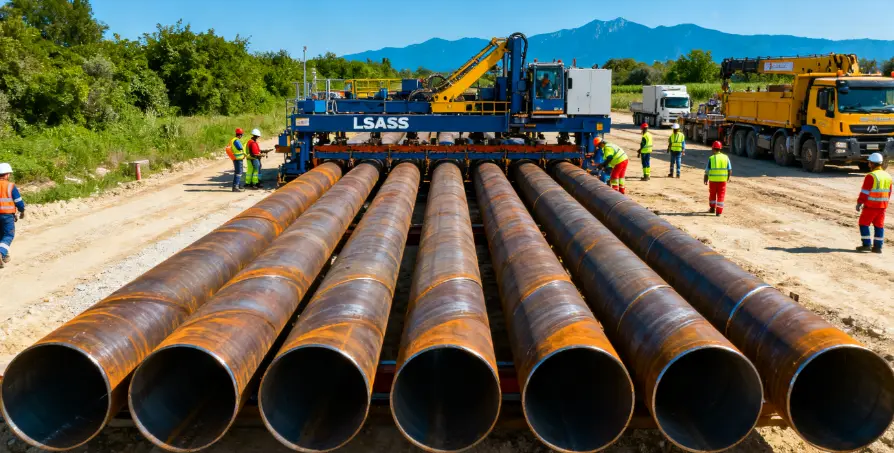
Combi Piles typically consist of large-diameter Steel Tubular Piles paired with steel sheet piles or infill plates, forming a continuous wall with excellent bending resistance and vertical load capacity. The steel tubes bear most of the structural load, while the sheet piles provide continuity and soil retention.
Comparison with Traditional Concrete/Drilled Piles
Unlike cast-in-place concrete piles, Combi Piles are fully prefabricated, eliminating the need for on-site concreting, curing, or slurry management. This not only accelerates construction but also improves predictability in challenging soil or marine environments.
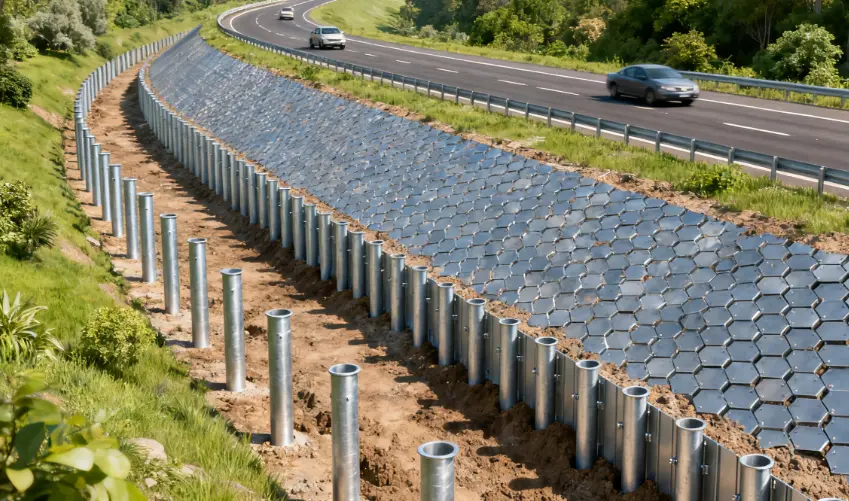

Construction Time & Cost Advantages
Speed Comparison: Combi Piles vs. Drilled Concrete Piles
The modular nature of Combi Piles allows for rapid installation using piling hammers or vibratory rigs. In a recent coastal retaining wall project, replacing conventional drilled piles with Combi Piles shortened the piling schedule by approximately 30%, with installation completed without weather-dependent waiting periods for concrete curing.
Transport, Installation & Concreting Cost Reduction
Because Combi Piles are factory-produced with precise dimensions, project teams reported about 20% savings in transportation and lifting costs. Eliminating concrete pouring reduces labor demands, machinery usage, and environmental disturbance—especially critical for marine or urban projects with strict noise and sediment control requirements.
Structural Performance & Application Scenarios
Strength, Deformation & Stability
Combi Piles provide high bending stiffness, strong deformation control, and improved sliding resistance—key requirements for retaining walls resisting earth pressure, tidal loads, or train-induced dynamic forces.
Typical Use Cases
-
Coastal and riverbank protection
-
Railway and highway embankment reinforcement
-
Port and harbor retaining walls
-
Deep excavation support near sensitive structures
These features make Combi Piles a preferred option in engineering environments where reliability and installation efficiency are equally important.
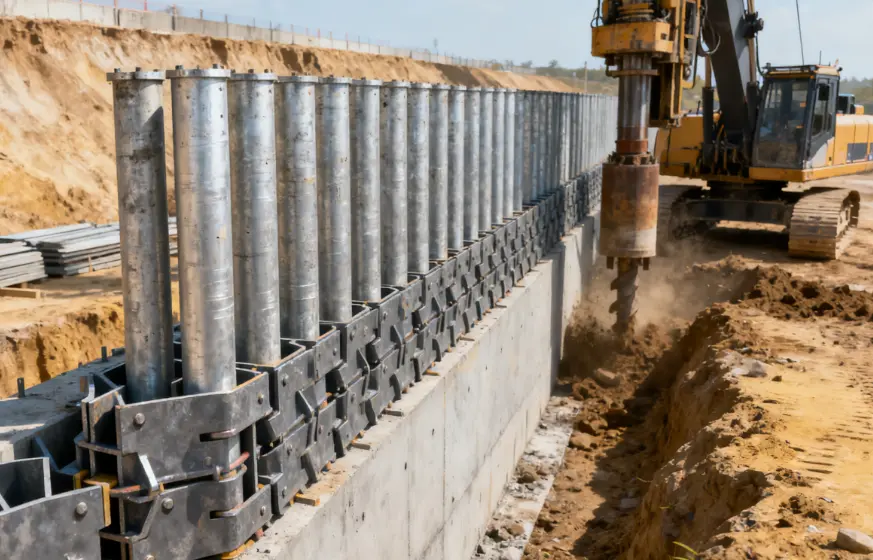

Design & Selection Recommendations
Material Specifications & Welding Requirements
Engineers should pay close attention to steel grade, wall thickness, pile end detailing, and welding quality. Whether using interlocks, sleeves, or full-penetration welds, connection integrity must meet required design standards.
Installation Notes
Key considerations include:
-
Proper pile spacing to meet deformation limits
-
Ensuring tight engagement between tubes and sheet piles
-
Temporary bracing or walers when necessary
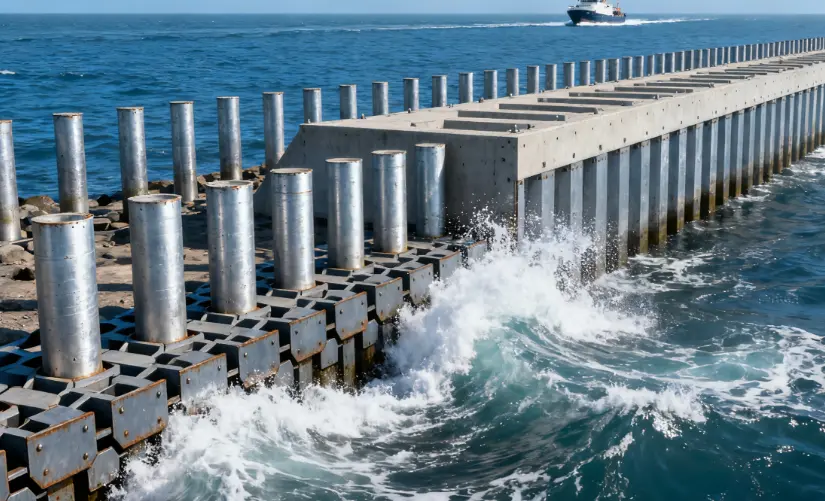

Case Highlight: Tubular Steel Coastal Retaining Wall Project
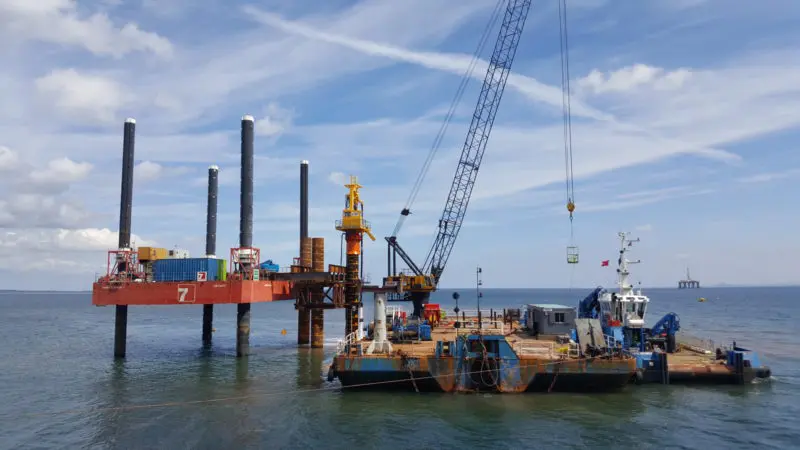
In a recent waterfront protection project supplied by Tubular Steel, the contractor replaced traditional bored piles with a steel-tube-plus-sheet-pile Combi structure. The results were clear:
-
30% reduction in piling schedule
-
20% lower transportation and lifting costs
-
Minimal on-site concrete work and reduced environmental disturbance
Procurement & Collaboration Advice
Example Inquiry Checklist
-
Steel pipe diameter, length, and wall thickness
-
Steel grade requirements (e.g., S355, S390)
-
Interlock type: cold-formed or hot-rolled
-
Welding or connector preferences
-
Coating or corrosion-protection needs
Key Questions to Discuss with Suppliers
-
Manufacturing tolerances and inspection standards
-
Delivery timelines and stock availability
-
Recommendations for installation equipment
-
Previous project references in similar conditions